Image Filters Panel
Filter image using different image filters.
Back to Index --> User Guide --> Panels
Contents
-
Brief video demonstration -
The Image Filter ▼ dropdown -
The Mode ▼ dropdown -
The Options ▼ dropdown -
Various settings for the filters -
The Filter button
Brief video demonstration
Use of filters in a brief video demonstration:
 MIB in brief: image filters (https://youtu.be/VwEPZxObA5U)
MIB in brief: image filters (https://youtu.be/VwEPZxObA5U)
Image filters were heavily updated and it is recommended to use new filters dialog available upon press of the New filters button
or from Menu-Image->Image filters>
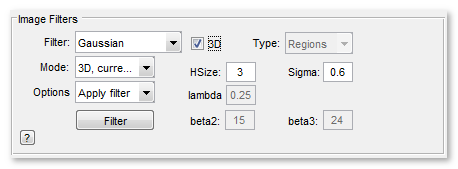
The Image Filter ▼ dropdown
Allows selection of a filter from a list of 2D and 3D image filters. Depending on the filter type some additional parameters should be specified in the HSize, Sigma, lambda, Type, Angle, and Iter edit boxes.
List of available filters:
-
Average, (2D) MATLAB Averaging filter, see more in the MATLAB documentation for
fspecialandimfilter -
Disk, (2D) MATLAB circular averaging filter (pillbox), see more in the MATLAB documentation for
fspecialandimfilter - DNN Denoise, (2D) denoise images using deep neural network, available for MATLAB R2017b and newer, requires Neural Network Toolbox and good GPU
-
Gaussian, (2D) MATLAB a rotationally symmetric Gaussian lowpass filter, see more in the MATLAB documentation for
fspecialandimfilter - Gaussian, (3D) is based on Dirk-Jan Kroon implementation and uses the fact that a Gaussian kernel can be implemented as several 1D kernels.
- Gradient, (2D/3D) generates gradient image
- Frangi, (2D/3D), Hessian based Frangi Vesselness filter. This function uses the eigenvectors of the Hessian to compute the likeliness of an image region to contain vessels or other image ridges , according to the method described by Frangi 1998, 2001. Implementation is based on Hessian based Frangi Vesselness filter, written by Marc Schrijver and Dirk-Jan Kroon.
-
Motion, (2D) MATLAB filter to approximate the linear motion of a camera, see more in the MATLAB documentation for
fspecialandimfilter. -
Median, (2D) MATLAB 2D median filter. Median filtering is a nonlinear operation often used in image processing to reduce "salt and pepper" noise. The median filter is more effective than convolution when the goal is to simultaneously reduce noise and preserve edges. See more in the MATLAB documentation for
medfilt2. -
Median, (3D) MATLAB 3D median filter (Release 2017a and later). Median filtering is a nonlinear operation often used in image processing to reduce "salt and pepper" noise. The median filter is more effective than convolution when the goal is to simultaneously reduce noise and preserve edges. See more in the MATLAB documentation for
medfilt3. A short youtube demo - Perona Malik anisotropic diffusion, (2D) - a filter written by Peter Kovesi to perform anisotropic diffusion of an image following Perona and Malik's algorithm. This process smoothes the regions while preserving, and enhancing the contrast at sharp intensity gradients.
-
Unsharp, (2D) MATLAB sharpens image using unsharp masking (
imsharpenfunction, R2013a and above) or unsharpens contrast enhancement filter (fspecialandimfilter, R2012b and older). -
Wiener, (2D) MATLAB 2D 2-D adaptive noise-removal filtering (
wiener2function).wiener2lowpass-filters a grayscale image that has been degraded by constant power additive noise.wiener2uses a pixel wise adaptive Wiener method based on statistics estimated from a local neighbourhood of each pixel. - External: BMxD, (2D/3D) an optional filtering by block-matching and 3D collaborative algorithm. The filters are not supplied with MIB and should be intalled separately, please refer to the installation instruction in the System Requirements section. Reference: K. Dabov, A. Foi, V. Katkovnik, and K. Egiazarian, "Image Denoising by Sparse 3D Transform-Domain Collaborative Filtering," IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 16, no. 8, August, 2007. preprint at <http://www.cs.tut.fi/~foi/GCF-BM3D http://www.cs.tut.fi/~foi/GCF-BM3D>. And M. Maggioni, V. Katkovnik, K. Egiazarian, A. Foi, "A Nonlocal Transform-Domain Filter for Volumetric Data Denoising and Reconstruction", IEEE Trans. Image Process., vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 119-133, January 2013. doi:10.1109/TIP.2012.2210725
Note! If HSize is specified with a single number then the size of the 3D Kernel is calculated based on pixel size of the dataset Menu-Dataset->Parameters>. If HSize is specified with 2 numbers (i.e. 3;3) then the Kernel size is [3 x 3 x 3].
The Mode ▼ dropdown
The Mode ▼ dropdown allows to select part of the open dataset to apply the filters.
- 2D, shown slice ▼, apply filter only for the currently shown slice
- 3D, current stack ▼, apply filter only for the currently shown stack
- 4D, complete volume ▼, apply filter for complete dataset
The Options ▼ dropdown
The Options ▼ dropdown allows to choose what to do with the dataset after filtration
- Apply filter ▼, this option filters the image and shows the result on the screen. It applies the selected filter to the image and displays the filtered image as the output
- Apply and add to the image ▼, this option filters the image and adds the result to the original image. It applies the selected filter to the image and combines the filtered image with the original image, resulting in a modified image that includes the filtered effect
- Apply and subtract from the image ▼, this option filters the image and subtracts the result from the original image. It applies the selected filter to the image and subtracts the filtered image from the original image, resulting in a modified image that removes or reduces the filtered effect
Various settings for the filters
Here is a set of edit boxes (3D, Type, HSize, lambda, Sigma, beta2, beta3) that define additional parameters for the filters. Depending on the selected filter one or more of these edit boxes may be disabled.
The Filter button
Press this button to start the filtering process.
Back to Index --> User Guide --> Panels