Image Morphological Operations
Back to MIB | User interface | Menu | Image
Description
Applies morphological operations to enhance or modify the dataset’s images, updating the Image layer.
The processed image can be added to or subtracted from the existing image, as specified in the operation settings.
Select the morphological operation from the dropdown. Configure the structuring element size and shape for applicable operations (e.g., dilation, erosion) in the and fields.
Choose how to handle the result using radio buttons in the Action to the result selecting:
- None, the resulting image will be direct result of the applied morphological operation
- Add to the image, add the resulting image to the current image
- Subtract from the image, remove the resulting image from the current image
Info
It is possible to enhance the resulting image by multiplying it using a factor provided
in the edit box.
The resulting image can also be smoothed with
and .
Click the button to preview the result,
or use the button to apply the selected
morphops to all images.
Tip
use to interactively follow results.
List of available morphological operations
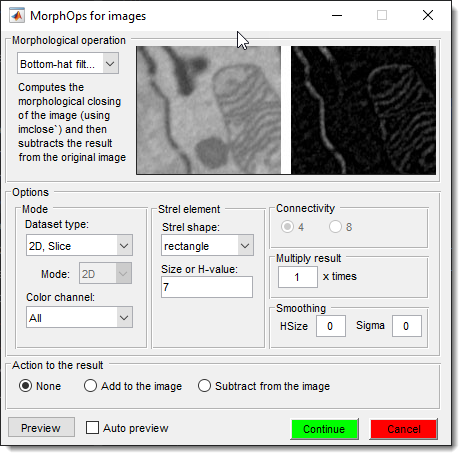
Bottom-hat Filtering
Computes morphological closing (imclose) and subtracts it from the original image, highlighting dark features smaller than the structuring element:
This operation is useful for enhancing dark regions or detecting small dark objects against a lighter background, such as pores or shadows in microscopy images.
Reference
imbothat at Mathworks.com
Clear Border
Suppresses light structures connected to the image border, removing unwanted edge artifacts:
Ideal for cleaning up datasets with bright boundary effects, ensuring focus on internal features.
Reference
imclearborder at Mathworks.com
Morphological Closing
Performs dilation followed by erosion, smoothing objects and closing small gaps:
This operation helps connect broken structures or fill small holes, maintaining object shapes in noisy datasets.
Reference
imclose at Mathworks.com
Dilate Image
Dilates the image, expanding bright regions and shrinking dark areas:
Useful for emphasizing or enlarging features, such as cell boundaries or bright spots, in preparation for further analysis.
Reference
imdilate at Mathworks.com
Erode Image
Erodes the image, shrinking bright regions and expanding dark areas:
Effective for removing small bright noise or thinning structures, enhancing contrast in dense datasets.
Reference
imerode at Mathworks.com
Fill Regions
Fills holes (dark areas surrounded by lighter pixels), creating uniform regions:
This operation is suited for correcting dark spots within objects, such as voids in cells or artifacts in solid structures.
Reference
imfill at Mathworks.com
H-maxima Transform
Suppresses maxima with height less than a specified H value, reducing minor peaks:
Useful for simplifying datasets by eliminating small bright spots while preserving significant maxima, aiding in feature detection.
Reference
imhmax at Mathworks.com
H-minima Transform
Suppresses minima with depth less than a specified H value, reducing minor valleys:
Helps clean up dark noise or small depressions, enhancing the visibility of deeper minima in intensity profiles.
Reference
imhmin at Mathworks.com
Morphological Opening
Performs erosion followed by dilation, removing small bright objects and smoothing boundaries:
This operation is effective for noise reduction and shape simplification, preserving larger structures.
Reference
imopen at Mathworks.com
Top-hat Filtering
Computes morphological opening (imopen) and subtracts it from the original image,
highlighting bright features smaller than the structuring element:
Ideal for detecting small bright objects, such as particles or highlights, against a darker background.
Reference
imtophat at Mathworks.com
Back to MIB | User interface | Menu | Image